Pachycormus discolor, Baja Elephant Tree





Scientific Name: Pachycormus discolor
Common Name: Baja Elephant Tree Spanish (Torote Blanco, Copalquín)
Also Called: Spanish (Torote Blanco, Copalquín)
Family: Anacardiaceae, Sumac Family
Synonyms: (Pachycormus discolor var. discolor, Schinus discolor)
Status: Native to Baja California.
Duration: Perennial
Size: 20 or 30 feet (6-9 m) tall and sometimes as wide; the trunk or multiple trunks become very large almost grotesque and may reach 24 to 32 inches (60-80 cm) in diameter.
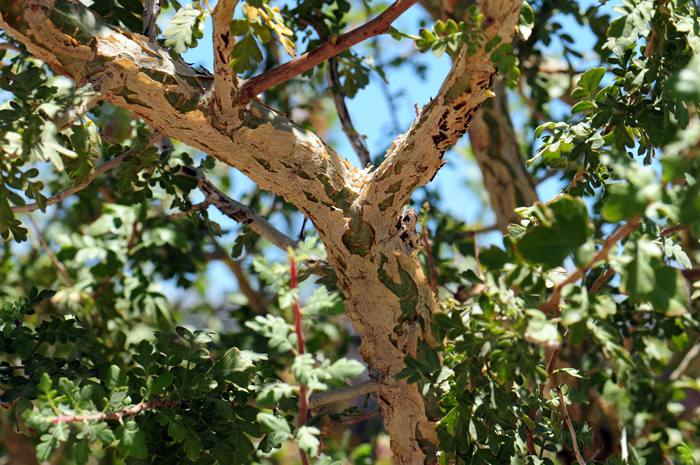
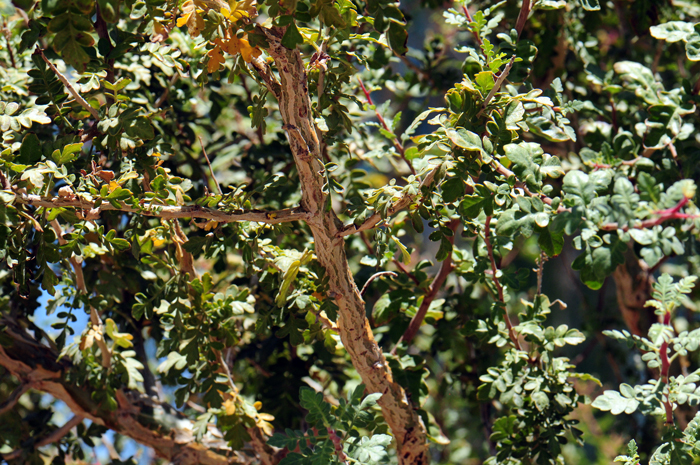
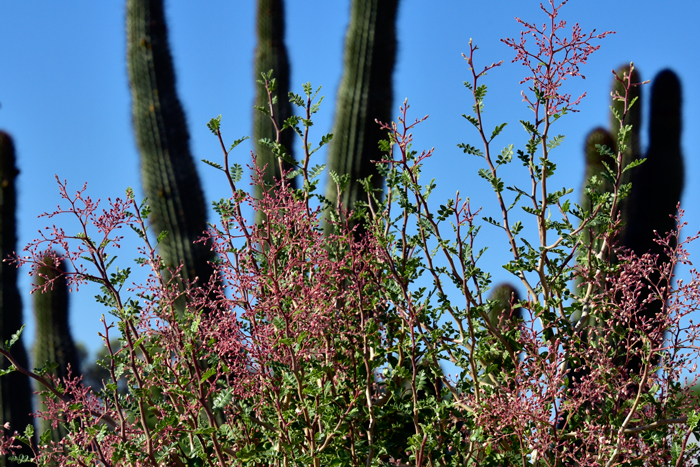
Growth Form: Tree or large shrub; a major characteristic is the large swollen-looking trunk (caudiciform) giving the plant the common name of Elephant Tree. Another characteristic is the older bark gradually turns gray, becomes thin and papery and peels off revealing the exposed bark, which is bluish-green in color and capable of photosynthesis; stems are grayish brown; stems drip a resinous sap if cut or damaged, more so under hot ideal growing conditions.
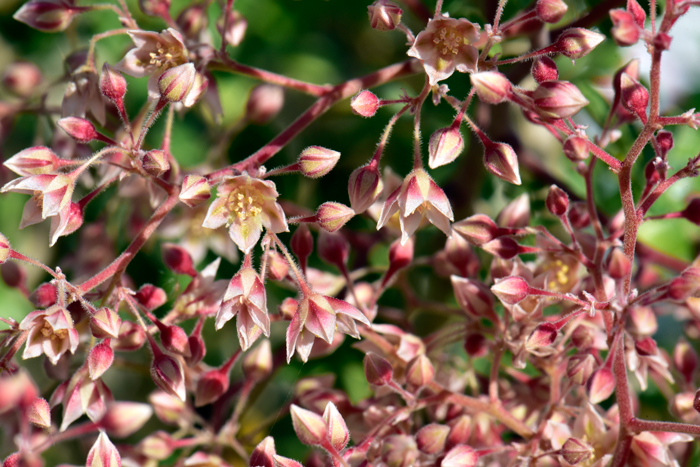
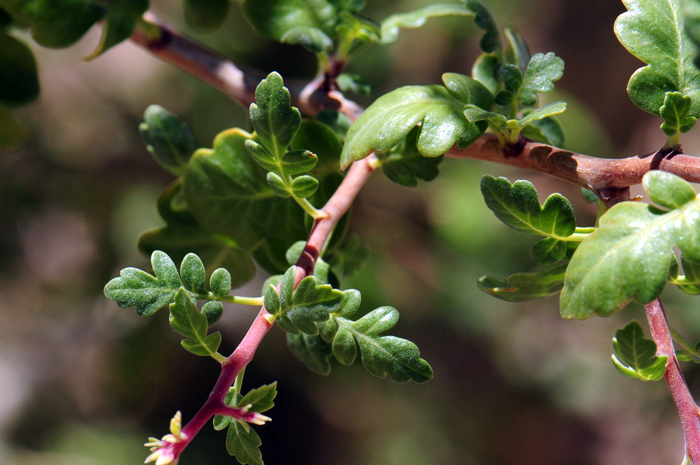
Leaves: Green, dark green, alternate; deciduous under hot summer conditions without moisture, pinnately compound, leaflets ovoid, margins often scalloped or entire; may grow up to 2 inches (5 cm) long under ideal circumstances, the terminal leaflet is mostly with 3-lobes as shown in the photo above; leaves pubescent,
Flower Color: Cream yellowish-white or pink flowers with pink center; small 5-petal and 5-sepal flowers in panicles or racemes as shown above; fruits small, dry and shaped like a bladder.
Flowering Season: May through September
Elevation: Sea Level to 4,500 feet (0-1371 m).
Habitat Preferences: Preferred habitats in Baja California are hillsides and lava fields where it is the most dominant plant.
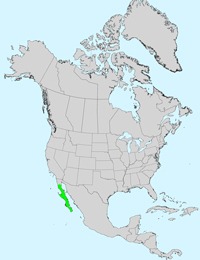
Recorded Range: Elephant Tree is native to North America and found exclusively in Baja California where it is most abundant in the central and southern portions. It has also been observed on Isla de Cedros.
USDA North America & US County Distribution Map for Pachycormus discolor. - No data available from USDA Plants Database.
Species distribution map for Pachycormus discolor:
Range map courtesy of Virginia Tech, Department of Forest Resources & Environmental Conservation
U.S. Weed Information: No information available.
Invasive/Noxious Weed Information: No information available.
Wetland Indicator: No information available.
Threatened/Endangered Information: No information available.
Tropicos includes 1 accepted species names 3 scientific names of infraspecific range for Pachycormus.
According to Tropicos there are 3 varieties in Pachycormus discolor;
Pachycormus discolor var. pubescens, white flowers, found on rocky slopes and plains, (Sierra de La Giganta);
Pachycormus discolor var. veatchiana, deep rose flowers, (Cedros Island and the western section of the Vizcaino Desert);
Pachycormus discolor var. discolor, (no information available).
It should be noted that some authors claim sub-species status as opposed to variety status.
In Southwest Desert Flora also see: Elephant Tree, Bursera microphylla. Bursera microphylla is similar looking species but actually belongs to the Burseraceae family, AKA the Elephant Tree or Torchwood Family.
The specific epithet "discolor" is originally from Middle English (1350–1400;) "discolouren" and later Latin "discolor" meaning to change color; become faded or stained, and refers to the pale bark.

